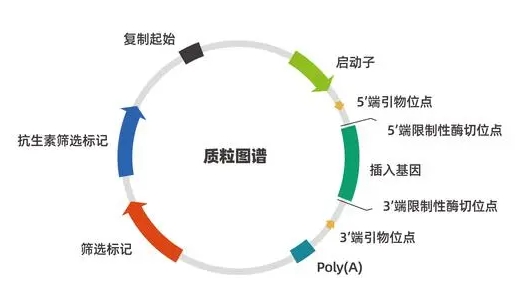
pESP-3酵母表达载体

The ESP? yeast protein expression and purification system uses the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe as the expression host and the glutathione S-transferase (GST) peptide as the protein purification tag. This system provides an easy alternative to protein production in E. coli. Proteins expressed in E. coli may lack proper biological function and antigenicity because of the absence of eukaryotic posttranslational modifications. S. pombe is a single-cell eukaryotic organism with properties similar to higher eukaryotic organisms. These properties, such as chromosome structure and function, cell-cycle control, RNA splicing and codon usage, make S. pombe ideal for the production of eukaryotic proteins. Also, eukaryotic proteins expressed in S. pombe are more likely to be folded properly, which improves the specific activity and can eliminate protein insolubility problems found in E. coli expression systems.
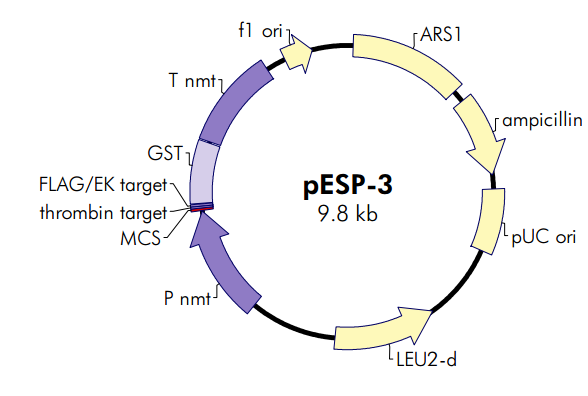
ARS1 origin 65–1270
ampicillin resistance (bla) ORF 1401–2258
pUC origin 2409–3076
yeast LEU2-d (promoter mutant) ORF 3909–5006
S. pombe nmt1 promoter 5945–7110
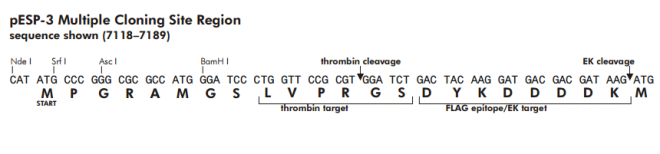
multiple cloning site 7118–7144
thrombin target 7145–7162
FLAG tag 7163–7186
EK target 7172–7186
GST affinity tag 7193–78406
S. pombe nmt1 terminator 7857–8851
f1 origin 9068–9374

基因搜项目发展历程最早可追溯至2010年01月05日域名注册,项目发起即为促进基因资源共享,避免在基因研究工作中“重复造轮子”,节约广大科研精英的宝贵时间和精力。
让基因研究更简单!
您值得信赖的一站式基因研究合作伙伴!